

Abhinav
Architecture of Docker
In simple terms, Docker is a software that helps in delivering of software packages in multiple isolated user spaces instances called containers. Before we jump into containers or docker in general, it is important to know what exactly is virtualization and how really it works.
VirtualizationWe all have heard about how we can run VMs or virtual machines on our systems. These Virtual machines (VM) is basically a virtual environment that works like a computer within a computer. It runs on an isolated partition of its host computer with its own CPU power, memory, operating system (such as Windows, Linux, macOS), and other resources.
For clearer interpretation of virtualization, let us consider a diagram having levels of virtualization:
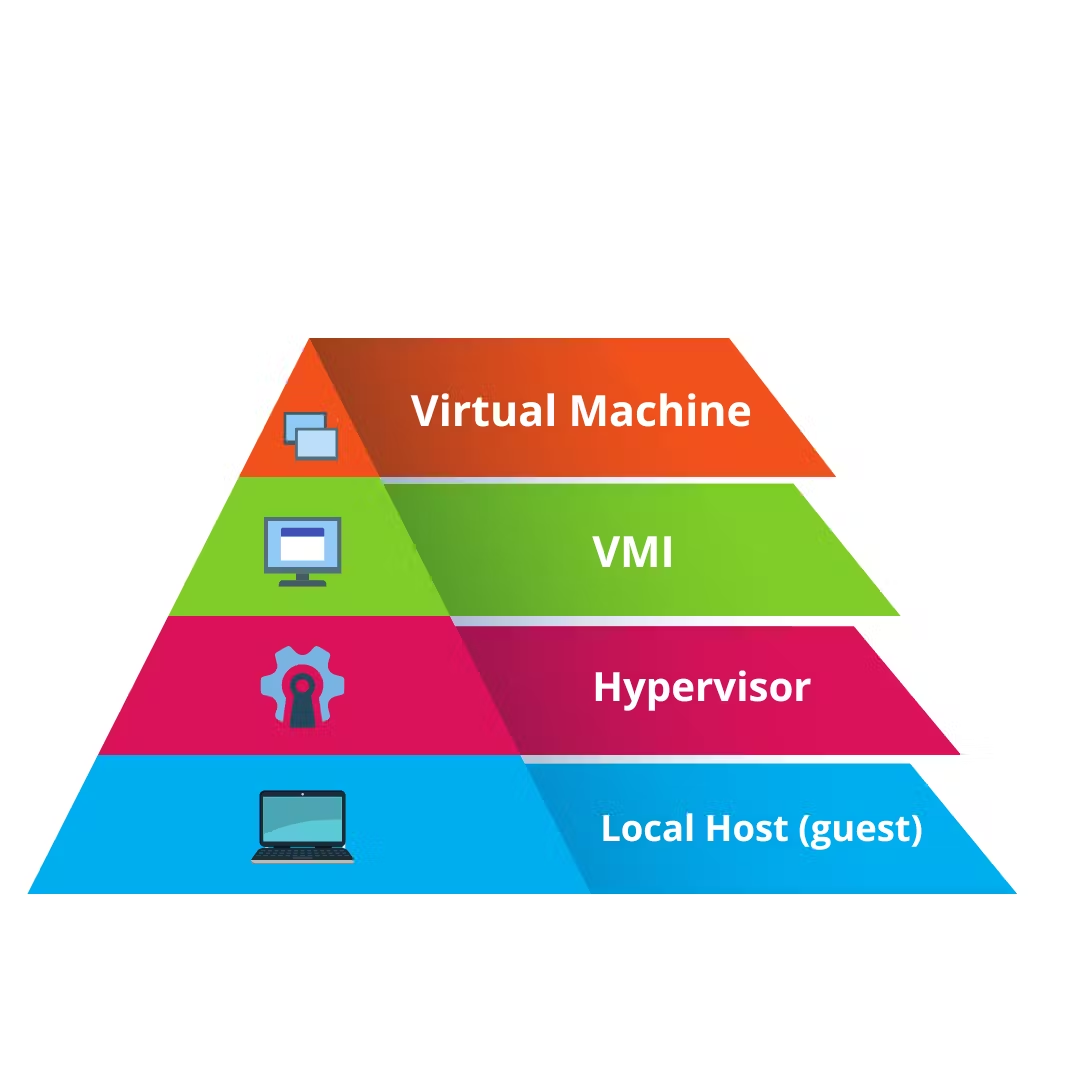
At the bottom, the physical machine is known as the host while the VMs running on it are called guests. We have our laptop on which we install a virtual box that gives us the environment and works as a hypervisor.
Hypervisors
These hypervisors run multiple VMI's over which VMs can abstracts guest machines and the operating system they run on, from the actual hardware. It create a virtualization layer that separates CPU / Processors, RAM and other physical resources from the virtual machines you create.
There are two types of hypervisors:
Then we have VMI (virtual machine images) over which the virtual machine runs which have their own separated OS and resources like memory from the main system.
Working of VM's:We now know how the overall system of virtualization works, now lets go deeper into what all things makes sure that the whole system works.
A VM comprises of these elements:
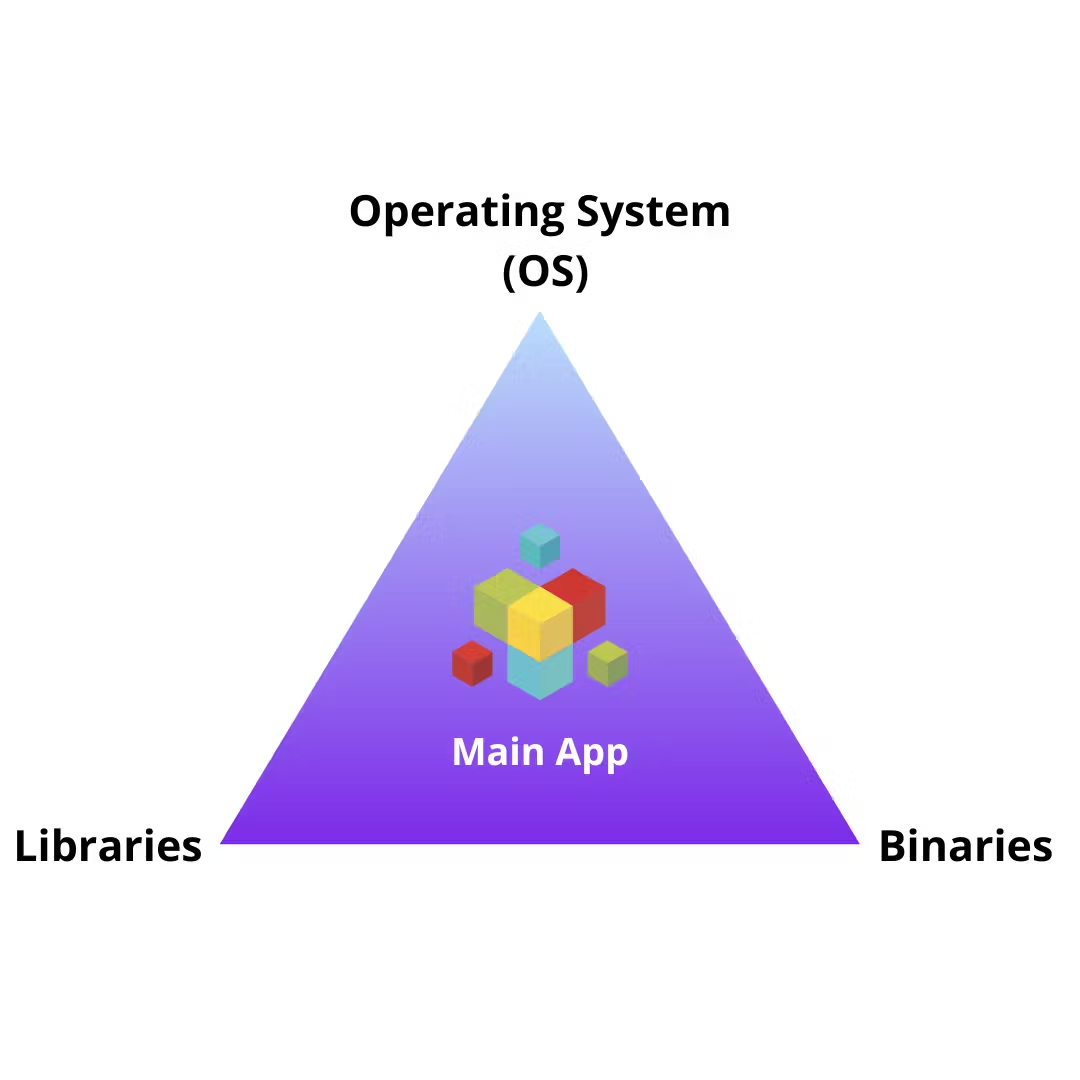
Each VM has its own Operating system.The resources needed to build them up are acquired from the system itself according to the needs which are controlled by namespaces which we will talk about later..
Now over this, there's another layer we should go to...
Container Layer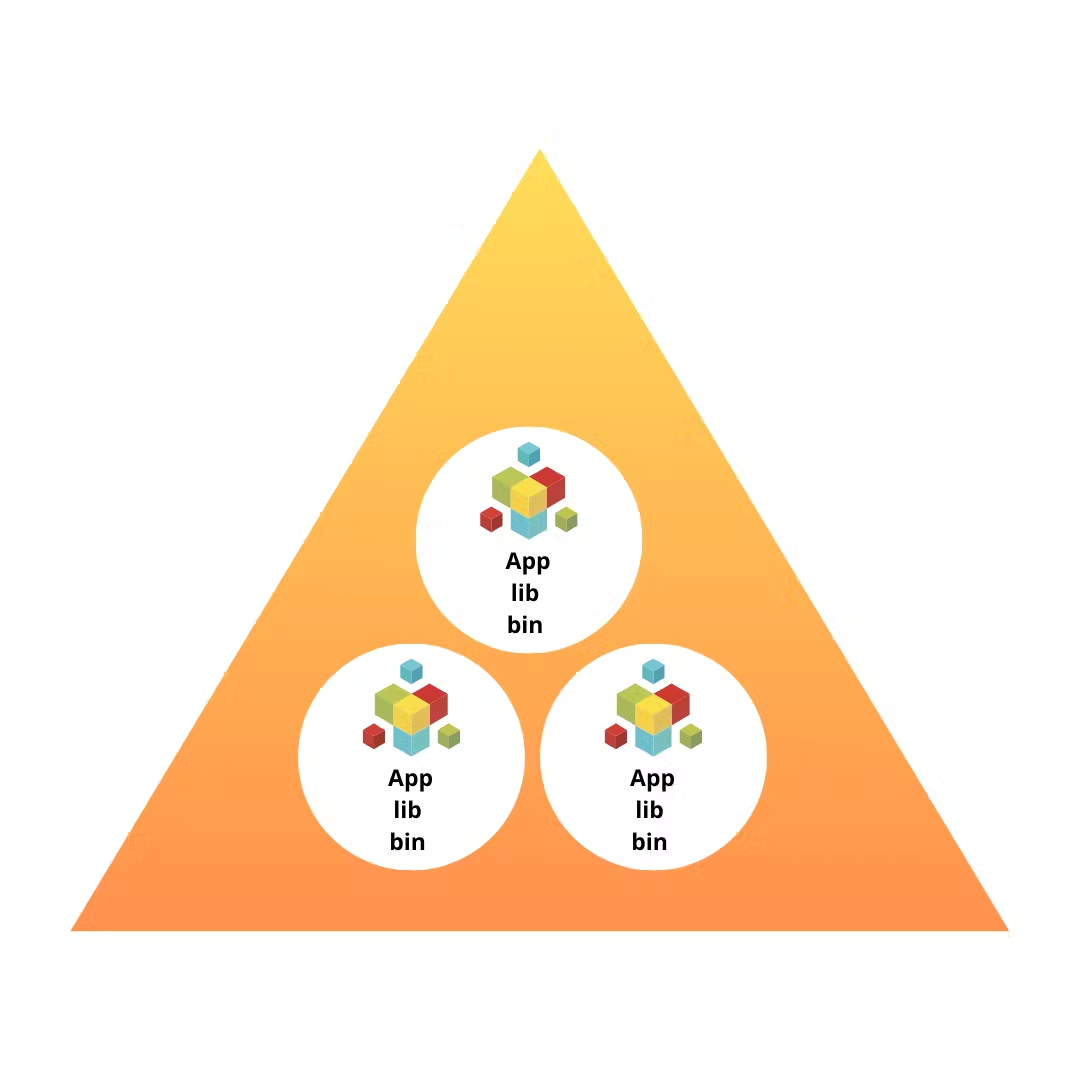
As you can see the "apps" which we discussed are now running together in a layer simultaneously. This layer is called a "container". These containers allows to encapsulate bins,libs and in running multiple apps on the same system. Therefore there is no need to create multiple operating systems for running multiple apps.
These containers have private space for processing, can execute commands as root, have a private network interface and IP address, allow custom routes and rules, can mount file systems.
With the help of containers, we can use and control namespaces and groups.
Namespace & Cgroups:To know about what are namespaces and groups, we should take a closer look back in app layer and see how encapsulation of app, bin and lib exactly happens.
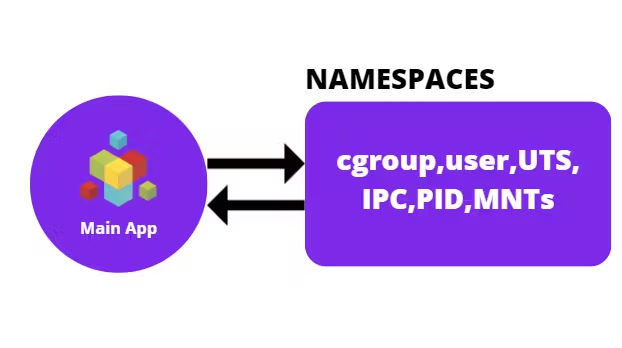
The encapsulation of all the components of a VM in which there are app,lib and bin are due to presems of namespaces.
Namespaces provide isolation of system resources, and cgroups allow for fine‑grained control and enforcement of limits for those resources. Docker uses namespaces to provide the isolated workspace i.e container. When you run a container, Docker creates a set of namespaces for that container which has many features as follows:
All of these features are available for VM's and all these VM's run on a layer known as containers and that too on a same system using a single system's operating system.
And finally these containers are used to test,deliver software packages across many users by the software called docker!
=============================================================